토비의 스프링을 읽다가...
스프링의 예외처리 방법 중 가장 대중적으로 많이 사용되는 ControllerAdvice의 동작원리를 한 번 알아보고 싶어서 정리해 본다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@RestControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionHandlerController {
@ExceptionHandler(ExampleException.class)
public ResponseEntity exception(ExampleException e) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR).body(e.getMessage());
}
}
|
cs |
개발 시 예외처리를 할 때 보통 이런 방식을 많이들 사용한다.
하나의 공식에 대입하듯이 기계적으로 사용하는 경우가 많은데..
스프링은 이 구조를 어떻게 처리하고 있는 것일까?
1. 최초에 DispatcherServlet에서 처리한다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
|
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = HttpMethod.GET.matches(method);
if (isGet || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new ServletException("Handler dispatch failed: " + err, err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new ServletException("Handler processing failed: " + err, err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
|
cs |
2. Exception 발생 시 dispatchException의 값을 변경한 뒤 processDispatchResult로 진입한다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,
@Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException mavDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = mavDefiningException.getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned.");
}
}
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
}
if (mappedHandler != null) {
// Exception (if any) is already handled..
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}
|
cs |
3. exception != null 인 경우, processHandlerException으로 진입한다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView processHandlerException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
// Success and error responses may use different content types
request.removeAttribute(HandlerMapping.PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);
// Check registered HandlerExceptionResolvers...
ModelAndView exMv = null;
if (this.handlerExceptionResolvers != null) {
for (HandlerExceptionResolver resolver : this.handlerExceptionResolvers) {
exMv = resolver.resolveException(request, response, handler, ex);
if (exMv != null) {
break;
}
}
}
if (exMv != null) {
if (exMv.isEmpty()) {
request.setAttribute(EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
return null;
}
// We might still need view name translation for a plain error model...
if (!exMv.hasView()) {
String defaultViewName = getDefaultViewName(request);
if (defaultViewName != null) {
exMv.setViewName(defaultViewName);
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using resolved error view: " + exMv, ex);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using resolved error view: " + exMv);
}
WebUtils.exposeErrorRequestAttributes(request, ex, getServletName());
return exMv;
}
throw ex;
}
|
cs |
해당 메서드에서 resolver.resolveException으로 진입하게 된다.
@ExceptionHandler를 통한 전역 에러 처리는 ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver가 담당하고 있다.
Spring mvc 사용 시 ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver, ResponseStatusExceptionResolver가 자동으로 등록된다.
이들을 순차적으로 실행하여 에러를 처리하기 위해 HandlerExceptionResolverComposite가 사용되는데,

resolver 목록을 순서대로 실행하여 resolver와 ModelAndView 값이 null이 아니면 ModelAndView를 반환한다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
@Override
@Nullable
public ModelAndView resolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) {
if (this.resolvers != null) {
for (HandlerExceptionResolver handlerExceptionResolver : this.resolvers) {
ModelAndView mav = handlerExceptionResolver.resolveException(request, response, handler, ex);
if (mav != null) {
return mav;
}
}
}
return null;
}
|
cs |
4. 주입받은 resolveException을 호출한다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
@Override
@Nullable
public ModelAndView resolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) {
if (shouldApplyTo(request, handler)) {
prepareResponse(ex, response);
ModelAndView result = doResolveException(request, response, handler, ex);
if (result != null) {
// Print debug message when warn logger is not enabled.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && (this.warnLogger == null || !this.warnLogger.isWarnEnabled())) {
logger.debug(buildLogMessage(ex, request) + (result.isEmpty() ? "" : " to " + result));
}
// Explicitly configured warn logger in logException method.
logException(ex, request);
}
return result;
}
else {
return null;
}
}
|
cs |
5. doResolveException 호출
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@Override
@Nullable
protected final ModelAndView doResolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (handler instanceof HandlerMethod hm ? hm : null);
return doResolveHandlerMethodException(request, response, handlerMethod, ex);
}
|
cs |
6. ServletInvocableHandlerMethod 주입
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
|
@Override
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView doResolveHandlerMethodException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Exception exception) {
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod exceptionHandlerMethod = getExceptionHandlerMethod(handlerMethod, exception);
if (exceptionHandlerMethod == null) {
return null;
}
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
exceptionHandlerMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
exceptionHandlerMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
ArrayList<Throwable> exceptions = new ArrayList<>();
try {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using @ExceptionHandler " + exceptionHandlerMethod);
}
// Expose causes as provided arguments as well
Throwable exToExpose = exception;
while (exToExpose != null) {
exceptions.add(exToExpose);
Throwable cause = exToExpose.getCause();
exToExpose = (cause != exToExpose ? cause : null);
}
Object[] arguments = new Object[exceptions.size() + 1];
exceptions.toArray(arguments); // efficient arraycopy call in ArrayList
arguments[arguments.length - 1] = handlerMethod;
exceptionHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer, arguments);
}
catch (Throwable invocationEx) {
// Any other than the original exception (or a cause) is unintended here,
// probably an accident (e.g. failed assertion or the like).
if (!exceptions.contains(invocationEx) && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Failure in @ExceptionHandler " + exceptionHandlerMethod, invocationEx);
}
// Continue with default processing of the original exception...
return null;
}
if (mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
return new ModelAndView();
}
else {
ModelMap model = mavContainer.getModel();
HttpStatusCode status = mavContainer.getStatus();
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(mavContainer.getViewName(), model, status);
mav.setViewName(mavContainer.getViewName());
if (!mavContainer.isViewReference()) {
mav.setView((View) mavContainer.getView());
}
if (model instanceof RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes) {
Map<String, ?> flashAttributes = redirectAttributes.getFlashAttributes();
RequestContextUtils.getOutputFlashMap(request).putAll(flashAttributes);
}
return mav;
}
}
|
cs |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
@Nullable
protected ServletInvocableHandlerMethod getExceptionHandlerMethod(
@Nullable HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Exception exception) {
Class<?> handlerType = null;
if (handlerMethod != null) {
// Local exception handler methods on the controller class itself.
// To be invoked through the proxy, even in case of an interface-based proxy.
handlerType = handlerMethod.getBeanType();
ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver resolver = this.exceptionHandlerCache.computeIfAbsent(
handlerType, ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver::new);
Method method = resolver.resolveMethod(exception);
if (method != null) {
return new ServletInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod.getBean(), method, this.applicationContext);
}
// For advice applicability check below (involving base packages, assignable types
// and annotation presence), use target class instead of interface-based proxy.
if (Proxy.isProxyClass(handlerType)) {
handlerType = AopUtils.getTargetClass(handlerMethod.getBean());
}
}
for (Map.Entry<ControllerAdviceBean, ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver> entry : this.exceptionHandlerAdviceCache.entrySet()) {
ControllerAdviceBean advice = entry.getKey();
if (advice.isApplicableToBeanType(handlerType)) {
ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver resolver = entry.getValue();
Method method = resolver.resolveMethod(exception);
if (method != null) {
return new ServletInvocableHandlerMethod(advice.resolveBean(), method, this.applicationContext);
}
}
}
return null;
}
|
cs |
7. 핸들러 invoke
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
if (returnValue == null) {
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
disableContentCachingIfNecessary(webRequest);
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
}
else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers");
try {
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatErrorForReturnValue(returnValue), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
|
cs |
정리하자면...
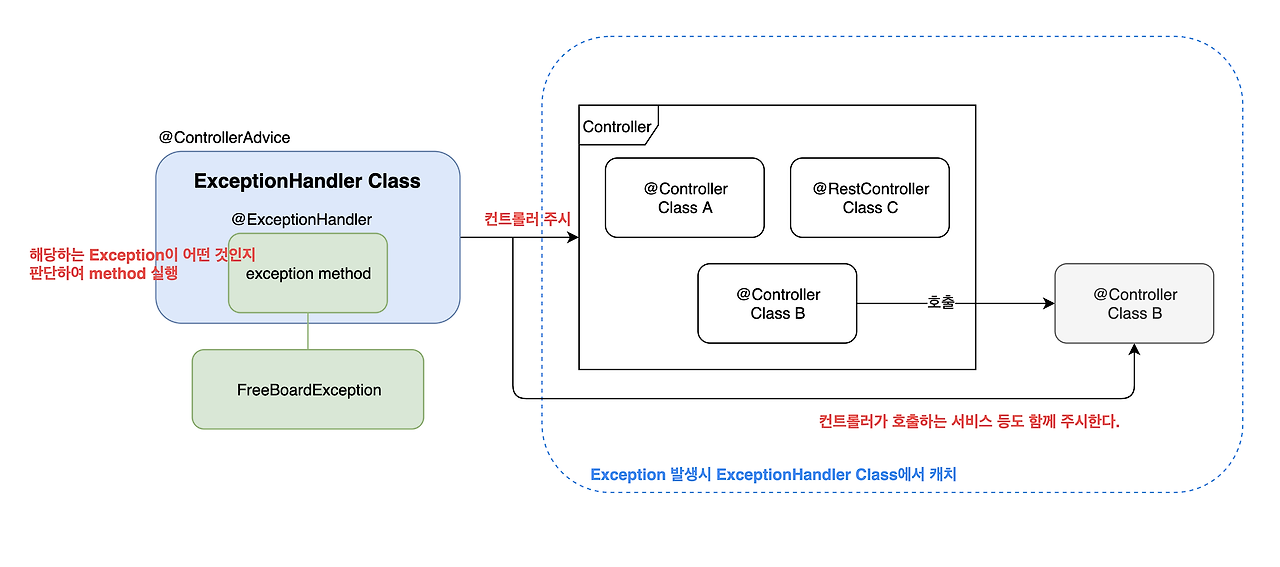
@ControllerAdvice, @RestControllerAdvice를 붙인 클래스는 Bean으로 등록된다.
@ControllerAdvice가 있는 클래스의 메서드 중 @ExceptionHandler가 선언된 메서드가 Contoller 실행 중 호출되면
해당 Exception을 반환한다.
이는 스프링의 AOP를 이용하여 예외처리를 함으로써 중복을 제거하고 일관성 있는 예외처리 관리를 가능하게 해 준다.
'BackEnd > Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring] Spring Bean 이란? (0) | 2022.10.10 |
|---|---|
| [Spring] @Transactional 제대로 알고 사용하기 (2) | 2022.10.03 |

댓글